Citation: Schneider A, “Towards User-Centric Specification of Autoinjector Technical Attributes: Insights From Empirical Work”. ONdrugDelivery, Issue 120 (May 2021), pp 39–42.
Andreas Schneider discusses an empirical study into both users’ ability to remove the cap from an autoinjector and the difficulty those patients perceived in doing so. The study builds a quantitative model relating the empirical data to patient perception.
Although user-centricity has been a guiding paradigm in the development of new drug delivery devices, little is known about how technical attributes of spring-actuated prefilled autoinjectors shape patient perceptions about the ease of handling them. To shed further light on the subject, Ypsomed conducted an empirical study1 that explored users’ ability to remove an autoinjector’s protective cap and quantitatively assessed how patient characteristics, such as dexterity, age, and sex, influence self-reported ease-of-use. In so doing, the empirical work provides much-needed insights into how clinically relevant technical attributes relate to user perceptions and, ultimately, device preferences. The study concludes with selected recommendations for new product development and considerations for device specification on the basis of patient-specific needs.
“A great deal is known about if and how autoinjectors can be used safely and effectively for their intended uses and use conditions. However, there is limited understanding of how user perceptions shape the specification of clinically relevant technical attributes of autoinjectors.”
PATIENT-CENTRICITY FROM WORDS TO ACTION
“Putting the patient at the centre of everything we do” may sound like a very bold statement, but this mindset has nevertheless permeated throughout drug delivery device development, be it with device manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies or regulators. In fact, patient-centricity has become the standard guiding paradigm in the development of new prefilled autoinjectors. For example, formative and summative usability studies have proved to be indispensable tools for effective new product development, and research has provided rich insights into how patients, caregivers and healthcare professionals administer drugs subcutaneously with the help of innovative self-injection devices.
A great deal is known about if and how autoinjectors can be used safely and effectively for their intended uses and use conditions. However, there is limited understanding of how user perceptions shape the specification of clinically relevant technical attributes of autoinjectors. The lack of relevant studies is surprising, given that industry is acutely aware how clinically relevant technical attributes may shape design preferences and drive treatment choices. A misleading specification of clinically relevant technical attributes may negatively impact the perception of the device, and also limit its safe and effective use.
The study discussed in this article1 puts the autoinjector cap-removal process under the microscope – a critical step for effective device use. Specifically, the empirical work studied whether patients, caregivers and healthcare professionals with a range of disabilities were able to remove the autoinjector protective cap with target removal force up to 55 N. The study also shows how the cap-removal force and participant characteristics, such as age, sex and dexterity impairment, shape self-reported perceived ease of cap removal, and ultimately device preferences.
REMOVE THE NEEDLE CAP FROM THE AUTOINJECTOR – INTRODUCING THE EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
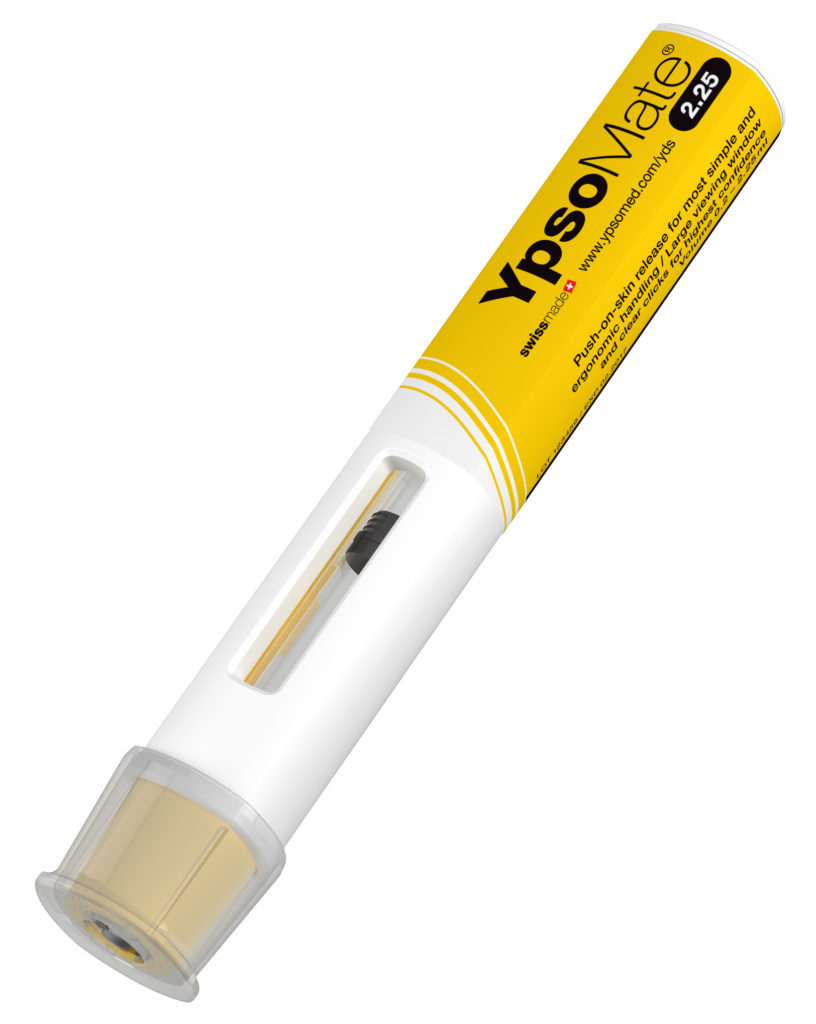
Figure 1: The YpsoMate 2.25 mL autoinjector platform included in the empirical study. The device platform is marketed as a prefilled two-step autoinjector device for Teva’s migraine-treatment drug AJOVY® (fremanezumab).
The single-site simulated-use study included 42 participants across five user groups:
- Adolescent patients
- Adult patients
- Elderly patients
- Non-professional caregivers
- Healthcare professionals.
Participants were sampled to assess the potential effects of user characteristics, such as dexterity, age, sex and professional education, on the cap-removal process. All patients were diagnosed with at least one chronic disease for which autoinjector-based drug products are being commercialised, such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes or multiple sclerosis. Each participant was asked to remove the protective needle cap of four non-functional devices with cap-removal forces in the range of 25–55 N. Effective task completion and user-reported ease of cap removal were documented for each cap-removal process.
The study included non-functional mock-up devices of the prefilled YpsoMate 2.25 mL autoinjector platform (Figure 1). The US FDA-approved and commercialised two-step YpsoMate 2.25 mL autoinjector is based on a push-on-skin principle to initiate the injection; users then sustain a minimum force to hold the device against the skin to complete the injection.
“Users whose hands were affected by rheumatoid arthritis reported higher discomfort when removing the autoinjector cap compared with other user groups – despite the fact that all users effectively removed the protective needle cap independent of dexterity impairments.”
CAP-REMOVAL FORCES OF UP TO 55 N ENABLE EFFECTIVE DEVICE USAGE
The empirical study shows that all participants were able to effectively remove the autoinjector cap with target cap-removal forces of up to 55 N with the YpsoMate 2.25 mL autoinjector and its unique protective cap design. Interestingly, and contrary to expectation, the upper limit of cap-removal force that might prevent effective device usage was apparently above the range included in the study. With respect to the ability to remove the cap of the autoinjector, no differences were found based on patient characteristics, such as age, professional education or dexterity impairments.
Although other studies have identified use difficulties and use errors due to the cap-removal process, the results of this study were consistent with earlier anthropometric research on finger pull strength. Here, scholars observed that healthy male volunteers applied up to 98 N when pulling with one hand on a device equipped with force sensors. Previous anthropometric work has also demonstrated the importance of a device design that accommodates different types of pinch grips to maximise the pull force. The results of the empirical study summarised here similarly underscores the need for flexible protective needle cap geometry to allow for different pinch grips during the cap-removal process.
TOWARDS A QUANTITATIVE MODEL FOR USER-CENTRED SPECIFICATION OF CAP-REMOVAL FORCE
In addition to the findings on users’ ability to remove the protective cap, the empirical work also modelled the relationship between the cap-removal force and user-reported ease of cap removal.
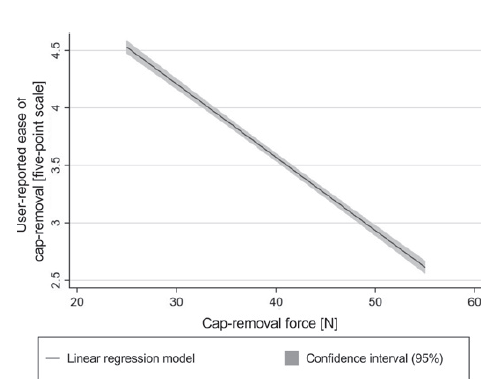
Figure 2: Graphical representation of the relationship between cap-removal force and user reported ease of cap removal.
This was done as a basis for a user-centred specification of cap-removal force. Specifically, users rated the perceived ease of cap-removal for each cap-removal process on a five-point scale (one being very difficult and five being very easy). A linear model was then built to quantitatively relate the cap-removal force to the user-reported ease of cap removal (Figure 2). The statistical analysis not only confirms a negative relationship between cap-removal force and user-reported ease of cap removal, but also quantifies this relationship. The results show that a 1 N increase in cap removal force results in a 0.064 point lower self-reported ease of cap-removal on the five-point scale. This model is a first step towards establishing a comprehensive toolbox for device development teams to predict user perception of clinically relevant device attributes, such as the cap-removal force. Consider an illustrative example. A cap-removal force of 25 N corresponds to a mean of 4.62 on the five-point scale for user-reported ease of cap removal. If the specification of this force was increased by 9 N, for example due to the use of an alternative rigid needle shield, it would still maintain an average value of 4.0 on the five-point scale for ease of cap removal.
USER CHARACTERISTICS MATTER WATCH FOR DEXTERITY-IMPAIRED PATIENTS
The linear model also uncovered a negative effect of dexterity impairment on perceived ease of cap removal. Users whose hands were affected by rheumatoid arthritis reported higher discomfort when removing the autoinjector cap compared with other user groups – despite the fact that all users effectively removed the protective needle cap independent of dexterity impairments. These findings are critical for the design and development of drug delivery devices for chronic debilitating disease states, such as multiple sclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis. This patient group is expected to be most sensitive to higher cap-removal forces, as this may have stronger effects on device perception and preference. In addition, cap-removal force deserves close attention as these disease areas are characterised by especially strong intra-class competition between treatment options.
EMPIRICAL INSIGHTS TO GUIDE FUTURE DEVICE DEVELOPMENT
The simulated-use study provided important insights for the user-centric specification of clinically relevant technical attributes, such as the cap-removal force. The results show that users were able to effectively remove the device’s cap with target forces up to 55 N. Because the study distinguishes between users’ ability to remove the autoinjector cap and their perceived ease of cap-removal, it provides a more nuanced understanding of the autoinjector cap removal process. As such, the simulated-use study provides a measure of how increasing the cap removal force reduces the user-reported ease of cap removal.
The resulting model is a starting point for building an advanced toolbox for predicting user perceptions based on device technical attributes. Finally, while the study suggests that dexterity impairment does not affect users’ ability to remove the protective needle cap, it reveals a negative effect of dexterity impairment on users’ perceived ease of cap removal. These insights have important implications for the design and development of new autoinjectors and injection devices, such as those developed by Ypsomed (Figure 3), as they re-emphasise the importance of involving users early in new product development.
Figure 3: Ypsomed’s leading portfolio of drug delivery device platforms to facilitate subcutaneous drug administration.
ABOUT THE STUDY
The empirical study summarised here was funded by Ypsomed and conducted in collaboration with Design Science (Philadelphia, PA, US). As a leading developer and manufacturer of self-injection systems for subcutaneous drug delivery, Ypsomed has established a scientific research & communications programme with the purpose of advancing new insights relevant to industry and academia. The results regularly appear in peer-reviewed scientific forums, such as Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, Patient Preference and Adherence, and Medical Devices: Evidence and Research, and are presented at leading medical device and drug delivery conferences, such as the PDA Universe of Prefilled Syringes and Injection Devices.
REFERENCE
- Schneider A et al, “User-Centric Approach to Specifying Technical Attributes of Drug Delivery Devices: Empirical Study of Autoinjector-Cap Removal Forces”. Patient Prefer Adherence, Feb 2021, Vol 15, pp 159–168.

