To Issue 152
Citation: Barichello E, “Biologic Integrity: Measuring and Managing the Hidden Leachables Risk from PFS Adhesive”. ONdrugDelivery, Issue 152 (Oct 2023), pp 88–92.
Enrico Barichello considers the often-overlooked influence of adhesive in the assembly of prefilled syringes and how the hidden risks can be managed and overcome.
“The presence of the adhesive introduces a potential contamination risk, as it is an additional substance in direct contact with the drug product.”
The growing prevalence of biologic drug products witnessed in recent years has been matched by a parallel increase in demand for prefilled syringes (PFSs) as the delivery mechanism of choice.
These innovative systems offer numerous key benefits, providing a precise pre-measured dose of a particular medication within a ready-to-use secure container. Beyond this, PFSs offer the advantages of reducing the risk of dosage errors, avoiding the potential for contamination caused by repeatedly inserting and withdrawing a syringe into a vial, and enhancing patient convenience in self-administration or autoinjector applications.
However, when it comes to biologics and biosimilars, the benefits of PFSs can only be realised if specific factors around safety and efficacy are considered. Generally, drug products of this nature present challenges around integrity and stability due to their sensitive nature. For example, in injectable form, the liquid formulation can be susceptible to degradation or contamination through interaction with the critical components that make up the primary packaging of the PFS.
In light of this, pharma companies and their delivery partners naturally put significant focus on the various elements that present a threat to the container closure system and have the potential to compromise the purity of the drug product within. Among these elements, however, there is one that remains relatively unexplored and uncharacterised in terms of its influence on drug integrity – the adhesive used in the assembly for staked-needle syringes.
CHALLENGES IN UNDERSTANDING SYRINGE GLUE LEACHABLES
With staked-needle PFSs, patient convenience and safety is increased as there is no requirement to attach a needle prior to delivery, which means time-consuming steps that could otherwise introduce human error are removed. To facilitate this, the adhesive plays a vital role in securing the needle to the glass in the cone of the syringe barrel. However, at the same time, the presence of the adhesive introduces a potential contamination risk, as it is an additional substance in direct contact with the drug product. In particular, it could result in leachable compounds migrating from the adhesive into the dose over time under normal storage conditions.
Adhesive leachables, such as acrylates, are problematic because they can potentially react with proteins and pose a risk to the integrity of the drug product. Given the sensitivity and complexity of biologic drug molecules, a comprehensive assessment of leachables is therefore essential to avoid undesirable interactions that could compromise drug quality or patient safety. This demands close control over the formulation, application and curing process of the needle adhesive, with a clear understanding of the interaction between the adhesive and the individual characteristics of the specific biologic formulation in question.
It might be assumed that such challenges can be overcome in large part through knowledge of the raw materials that constitute the adhesive, and suppliers are indeed likely to be able to provide preliminary extractable data relating to the ingredients used to form the adhesive compound. However, while this information should form part of the overall assessment, it does not account for the parameters associated with the final gluing and curing process, which, critically, can introduce new compounds that could impact the extractables profile and pose a risk to the purity of the drug product over time.
“The evaluation of syringe-glue compatibility should ideally be carried out early in the development process to avoid the possibility of subsequent complications and delays.”
ADDRESSING SYRINGE-GLUE COMPATIBILITY
Pharma companies therefore face a situation where they must, in the interests of efficacy and patient safety, interrogate their choice of syringe platform in its market-ready state for the risk of extractables. Furthermore, the evaluation of syringe-glue compatibility should ideally be carried out early in the development process to avoid the possibility of subsequent complications and delays. In following this path, crucial questions emerge – What testing process should be followed? Does the chosen syringe platform allow for customisation to address any concerns that might be identified? Where should the process begin?
Stevanato Group undertook a project on behalf of one customer that provided important responses to these challenges based on a comprehensive assessment of the parameters involved in the gluing process. This work encompassed anticipation and management of potential issues that may arise in relation to leachables, including a tailored approach to resolving interaction-related concerns.
The project employed the design of experiments approach and method development in order to evaluate the influence of relevant variables and identify specific glue-derivative compounds that may interact with the drug product. This resulted in the creation of a series of experiments that accurately recreated the conditions being assessed and allowed for high-impact process parameters to be tested using varying values.
ENSURING PRECISE TESTING AND ANALYSIS
In any scientific approach to testing and analysis, precision is critical to the quality of the results. In this case, Stevanato Group’s in-house manufacturing equipment was used to develop a dedicated bench-top unit, upon which all experimental activities were conducted with meticulous attention to methodological detail. To ensure that the findings from the test correlated with authentic manufacturing processes, the bench-top unit was also calibrated in line with the real-world machinery used for needle assembly (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Both processes, industrial and bench top, employ a system using LED lights for the core task of curing the adhesive.
Both processes, industrial and bench top, employed a system using LED lights for the core task of curing the adhesive. This approach was designed to deliver improvements in the polymerisation process while also reducing the levels of energy consumption required.
A principal objective of the testing activities was the screening, detection and analysis of various potential extractables. As such, the Stevanato Group Technology Excellence Centers developed multiple techniques capable of quantifying the presence of glue-based compounds, such as acrylic acid, in the final cured adhesive. These techniques included high performance liquid chromatography and ion chromatography.
By optimising the parameters of the curing process through changes in curing impulse and energy, the tests allow the Technology Excellence Centers to determine the nature of the relationship between the curing method and any extractables observed. This provided the insight that is necessary for customising the adhesive curing method for a specific drug formulation, ultimately allowing adaptations to be made that minimise the risk of adverse interactions and ensure the highest level of drug product quality and patient safety.
CUSTOMISABLE APPROACH FOR OPTIMAL RESULTS
In both cases, the levels of extractables –measured in ng per syringe – varied with each of the different adhesive curing combinations (Figures 2 and 3). Generally, higher curing energy facilitates better polymerisation of the glue, resulting in lower values of extractables. However, it is noteworthy that this relationship does not apply universally to all extractables. Rather, there is the potential for certain extractables to display unique behaviours that would require specific adjustments to be made to the curing process parameters to maintain extractable levels within a desirable threshold.
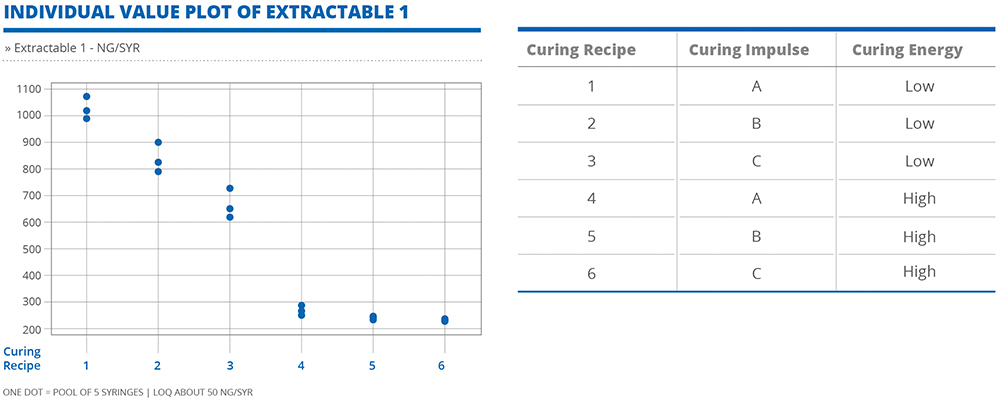
Figure 2: Generally, higher curing energy facilitates better polymerisation of the glue, resulting in lower values of extractables.
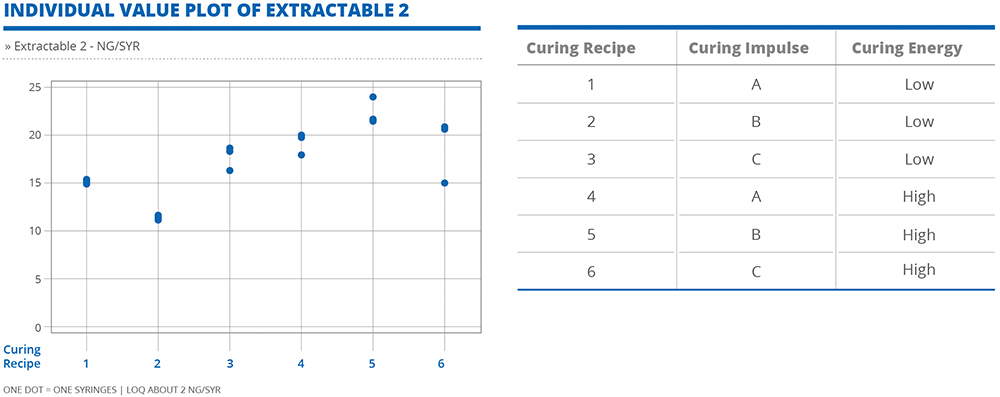
Figure 3: For certain extractables, higher curing energy does not result in lower values of extractables.
“A customised approach, based on specific drug formulation requirements, allows for the precise manipulation of curing impulse and energy to minimise the risk of adverse interactions and ensure the highest level of drug product quality and patient safety.”
These insights emphasise the complexity of the curing process and the diverse behaviours of extractables in relation to curing. This underlines the importance of taking a nuanced and tailored approach to the management of this risk, wherein a thorough evaluation of individual extractables is necessary to refine the adhesive process for optimal results. A customised approach, based on specific drug formulation requirements, allows for the precise manipulation of curing impulse and energy to minimise the risk of adverse interactions and ensure the highest level of drug product quality and patient safety.
Stevanato Group can help drug manufacturers effectively address potential leachables issues through an approach that combines quality components with customised support as part of an integrated offering. The foundation for this approach is provided by the Alba® and Nexa® syringe platforms. Both platforms have been designed to incorporate properties that mitigate the risk from extractables. Alba® syringes have been optimised specifically for applications involving high-value sensitive injectables, thanks to the addition of a specific internal coating (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Alba® syringes – Stevanato Group’s breakthrough solution for biologics.
When employing these products, pharma customers will know that every aspect of the individual components that form the complete system has been developed with consideration not only for injectable performance, but also for supporting the stability and integrity of the drug product. This, of course, includes the adhesive used in the needle assembly.
But, as the study results have shown, drug products cannot be expected to demonstrate universal properties when it comes to containment. The risk of leachables from adhesives will vary depending on the specific formulation in question. This means that a level of customisation is essential to arrive at an adhesive curing process that minimises the risk of compromising a given drug’s integrity by the presence of extractables.
The testing methodology described here provides the basis for analysing this risk for an individual API, employing the skills and knowledge of Stevanato Group’s in-house engineering team. This analysis opens the door to iterative development work, where the parameters of the adhesive curing process can be modified to address extractable levels. Thanks to the close integration between product teams, engineering teams and materials suppliers, as well as the ability to draw on previous experience of this process, Stevanato Group has the capabilities assist customers in arriving quickly at a compatible solution for protecting their high-value drug products.
CONCLUSION
While it might not be an aspect of containment that attracts significant attention, consideration of leachables in syringe adhesive can be of paramount importance when it comes to PFS applications involving biologic drug products. The evidence from testing conducted by Stevanato Group shows that it has the potential to influence the levels of extractables in ways that might not be well understood, as well as in ways that will be specific to a given drug. It is only through a clear understanding of the interaction between adhesive and drug, and a focused approach to customising the curing process, that this relatively hidden risk can be managed and mitigated, avoiding any compromise to drug quality and patient safety.
Find out more about Stevanato’s assembly lines for injection devices at: www.stevanatogroup.com/en/offering/assembly-equipment.

